The development of Web 3.0 is expected to be the next internet paradigm shift in many business models in the nearest future. There is a great deal of controversy about Web 3.0 and its impact on various business models. Web 3.0 is expected to impact both consumers and companies significantly. When it comes to the way people work, play, and do business, it will profoundly affect all aspects of daily lives. Knowledge-centric forms of computing are becoming more prevalent in Web 3.0. People and technology will interact, grow, exchange, and utilize information unprecedentedly and in new ways in Web 3.0. It will also be possible to achieve considerable gains in capabilities and life cycle economics via cost savings, greater efficiency, enhanced effectiveness, and new previously unachievable features. The paper examines how these evolutions of technologies, starting from web 1.0 to web 3.0, may create new value and new business models. With the advent of semantic web technologies, new business models based on direct and indirect income streams have evolved. Businesses are now moving fast to the adoption of web 3.0 due to the competitive advantage it embraces in business. Therefore, the paper will focus on using case representatives to explain how the evolution of web technology may be a significant milestone for the current and future business models.
The Evolution of Web Technology and Business Models
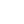
Although the internet fuels digital transformation, the technology has evolved well beyond its basic limitations. Since its debut more than two decades ago, the web has been subjected to rising centralization and mass monitoring degrees. Consequently, giant firms, governments, and news organizations continue to reap the benefits of the evolving web infrastructure designed to benefit all of mankind. The internet began with simple "read-only" technology, allowing users to browse and read the content. This Web 1.0 environment served largely as an extension of local retailers for advertising reasons. Web 2.0 users may now produce content and engage with the internet more deeply due to "read-write" capabilities with the newer web version of the technology. The web 2.0 infrastructure influences global business models by supporting the rapid rise of social media platforms, blogs, and online reviews. However, such rapid web technology changes have not been without their drawbacks. As online monitoring supports profitable data collecting, consumer safeguards fall behind corporate objectives. Ongoing data breaches effectively highlight the major drawback of this web 2.0 technology. In response to these difficulties, Web 3.0 efforts seek to reclaim authority for individuals in the current era.
Additionally, it represents the progression of web use and interaction, which involves the conversion of the internet into a database. After a lengthy period of focusing on the front-end, it allows the web's back-end to be upgraded. Web 3.0 encompasses a variety of web users and interface evolutions. Data is not owned in this case; instead, it is shared with multiple views for the same site/data shown by multiple programs. The Semantic Web (3.0) offers a more logical manner than Google's current engine schema can ever do. Web 2.0 involves the use of a declarative modal language like OWL to create domain-specific models that computers may use to reason about data and draw new conclusions, rather than merely matching keywords.
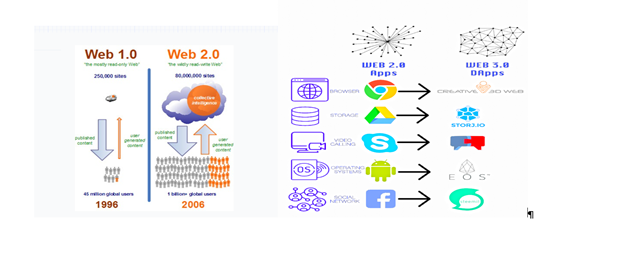
Visual Presentation of Evolution of Web 1.0 to Web 3.0 and Business Models
Any website or program that allows users to create and share online content is considered part of the Web 2.0 movement. The ability to create, share, cooperate, and communicate is one of the most important features of this technology. People may easily develop, publish, and share their work with the world using Web 2.0, which sets it apart from previous websites. They don't need any web design or publishing abilities to participate. Because of the nature of this technology, it is a simple and popular method of disseminating information to a small group or a much larger audience. Web 2.0 applications include wikis, blogs, networking sites, folksonomies, podcasting, and content hosting services, to name just a few examples (Aghaei). Wikipedia, YouTube, Facebook, and MySpace are among the most popular Web 2.0 sites.
How Web 3.0 Generates Value
In Web 3.0, computers collaborate with people to construct knowledge and make decisions, converting the internet infrastructure from a supporting to a protagonist entity in the development of content and processes. Therefore, allowing people and computers to collaborate on complex problem-solving and knowledge-creation projects. As a result of its assertiveness and high personalization, Web 3.0's processing capability allows it to provide consumers and companies with services and products of a high added value.
Additionally, the web 3.0 technology also sheds light on businesses, especially marketing. The growth of the internet has led to a shift in the marketing landscape. When web-ad banners first appeared on websites in the mid-1990s, Web 1.0 was the first to embrace "digital marketing." Likewise, social media was born with web 2.0 (Wetsch and Pike). As a result, firms and organizations have resorted to online promotion and advertising to expand their market share and effectively reach their target audience. However, there are significant drawbacks to Web 2.0, including the fact that a small number of large firms dominate the whole internet, the involvement of numerous intermediaries in the process, a lack of transparency, and the internet's confinement to screens alone. With the advent of web 3.0, marketers now have the tools they need to link their businesses with their target audiences effectively. Transparency, fraud prevention, and the elimination of the need for centralized data collecting are all possible outcomes of blockchain technology (Potts and Rennie). Instead of chasing views, fixing problems, and treating people like targets, web 3.0 will focus on tailoring the user's experience to the message being conveyed. As a result, marketers, and advertisers can reconnect with their customers by giving them control and ownership over their data and offering them real-time support on the services being offered.
The primary objective of Web 3.0 is to return control to internet users. Instead of handing over personal data to giant organizations, individuals build and run their tools. A decentralized web is not reliant on a large number of third parties. Web 3.0's most significant privacy improvement is the removal of centralized third parties from the equation. Rather than depending on firms like Facebook, users will engage in direct communication. This eliminates the possibility of a third party listening in on private communications. It is achievable owing to a few crucial technologies supported by Web3.0 technology. To keep social networks going without a centralized authority, incentive systems encourage members to engage. Communications are decentralized because no one party owns the blockchain. In addition, blockchains allow individuals to authenticate their identities on their own, reducing the number of persons who may access private data.
Web 3.0 will promote transparency in business transactions, operations, and payment processing using artificial intelligence systems with a decentralized storage approach. Web 3.0 will make the internet more open and honest. Aside from the fact that they cannot be altered, the data contained in a blockchain is also publicly accessible. Users will see exactly how their data is being used when web applications operate on this technology. As a result, users are frequently unaware of how different websites acquire, retain, and utilize their personal information, leading to privacy breaches that they weren't expecting. Because of its openness, a blockchain may help lift this shroud. Internet users will be able to make better decisions without uncertainty and misunderstanding.
There has also been a rise of less susceptible web technologies that are less likely to target cybercriminals. Using web 3.0, hacking would be far more complex. A hacker has to get access to at least 51% of the machines on the blockchain network to compromise it due to the technology's distributed nature. Rare though they may be, 51 percent of assaults need extensive logistical, hardware, and monetary resources. Users do not have to be concerned about their personal information being hacked because of this feature of blockchain technology. Therefore, increasing the size and complexity of these blockchain networks will reduce the likelihood of 51 percent cyber-attacks on internet-powered platforms.
Mainstreams Models That May Become Web 3.0 Business Models
The need for payment tokens is expected to expand, requiring the usage of web 3.0 technologies. There has been a noticeable lack of repeatability and scalability in the first ten years of Web 3.0 business models. Even if there is some doubt regarding their feasibility, humans are certain that the constant testing by some of the best builders will lead to valuable models being produced in the following years. Additionally, an emerging economic model for decentralized networks is the work token, which focuses only on the supply side of the network's income generation to lower costs for users (Potts & Rennie, 2018). REP and KEEP coins from Augur and Keep network are nice examples. As in the case of taxi licenses, service providers are required to put up a specific quantity of tokens to be granted the privilege of working for the network in return for a share of the profits. When using the labor token paradigm, actors may be rewarded with both a carrot and a stick for their efforts. Aside from encouraging service providers to do honest work, they may also get assessed by predicting future cash flows of service providers, which provides further network security.
It is evident that although conventional venture capital is still relevant, the nature of the investor and the nature of capital itself is changing due to the proliferation of new business models being developed as a result of rapid change of technology. As additional technical capabilities are added to Web 3.0, it is reshaping the web's technology in ways that will benefit a wide range of business models. Web 3.0 established a solid basis for companies with a technology bent. An investment in web 3.0 technology would give the company a competitive edge, allowing it to develop more quickly and more effectively.
 Web3News
Web3News